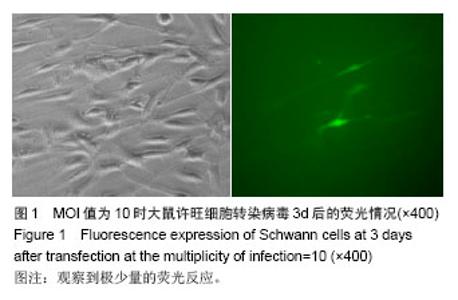
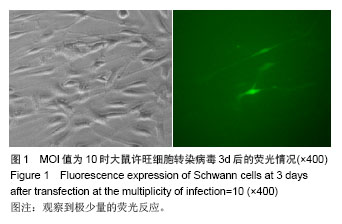
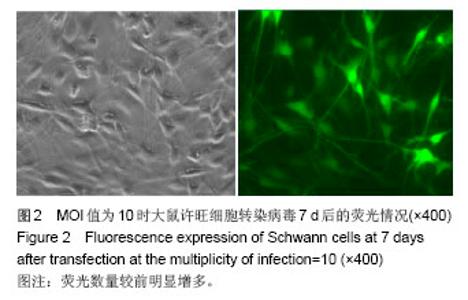
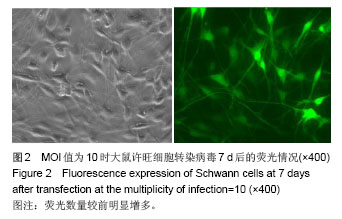
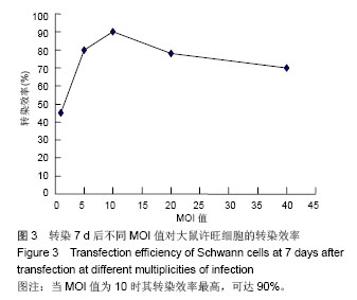
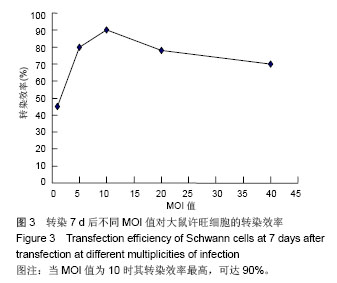
| [1]Richardson PM,McGuinness UM, Aguayo AJ. Axons from CNS neurons regernerate into PNS grafts. Nature.1980;284: 264-265.
[2]Martin D, Robe P, Franzen R, et al. Effects of Schwann cell transplantation in a contusion model of rat spinal cord injury. Journal of Neuroscience Research.1996;45: 588-597.
[3]Tuszynski MH, Weidner N, McCormack M, et al. Grafts of genetically modified Schwann cells to the spinal cord: survival, axon growth, and myelination. Cell Transplantation.1998;7: 187-196.
[4]Azanchi R, Bernal G, Gupta R, et al. Combined demyelination plus Schwann cell transplantation therapy increases spread of cells and axonal regeneration following contusion injury. Journal of Neurotrauma.2004;21: 775-788.
[5]Bunge RP. Expanding roles for the Schwann cell: ensheathment, myelination, trophism and regeneration. Curr Opin Neurobiol.1993; 3: 805-809.
[6]Xu XM, Guenard V, Kleitman N, et al. A combination of BDNF and NT3 promotes supraspinal axonal regeneration into schwann cell grafts in adult rat thoracic spinal cord. Exp Neurol.1995,134:261-272.
[7]鲁凯伍,陈哲宇,侯铁胜,等.胶质细胞源性神经营养因子对脊髓损伤后皮质脊髓束再生的保护作用[J].第二军医大学学报, 2002; 23(2):153-155.
[8]Zong HB, Zhao HX, Zhao YL, et al. Nanoparticles carrying neurotrophin-3-modified Schwann cells promote repair of sciatic nerve defects. Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(14): 1262-1268.
[9]Pan S, Wan JZ, Liu SS, et al. Lentivirus carrying the Atoh1 gene infects normal rat cochlea. Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(17): 1551-1559.
[10]Weidner N, Blesch A, Grill RJ, et al. Nerve Growth Factor–Hypersecreting Schwann Cell Grafts Augment and Guide Spinal Cord Axonal Growth and Remyelinate Central Nervous System Axons in a Phenotypically Appropriate Manner That Correlates With Expression of L1. Comp eurol. 1999; 413: 495–506.
[11]Sorensen J , Haase G, Krarup C,et al.Gene transfer to Schwann cells after peripheral nerve injury :a delivery systemfor therapeutic agents. Ann Neurol.1998;43(2):205-211.
[12]Hu Y,Leaver SG,Plant GW,et al. Lentiviral-Mediated Transfer of CNTF to Schwann Cells within Reconstructed Peripheral Nerve Grafts Enhances Adult Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axonal Regeneration. Mol Therapy.2005;11(6): 906-915.
[13]Dong L, Han CX, Zhang HZ, et al. Construction of a recombinant lentivirus containing human microRNA-7-3 and its inhibitory effects on glioma proliferation. Neural Regen Res. 2012; 7(27): 2144-2150.
[14]Zhu Y, Feuer G, Day SL, et al. Multigene lentivirus vectors based on differential splicing and translational contro1. Mol Ther. 2001;4(4):375-382.
[15]Buchschacher GL Jr , Wong-Staal F. Development of lentiviral vectors for gene therapy for human diseases. Blood. 2000;95 : 2499-2504.
[16]Hurtado A, Moon L, Maquet V, et al. Poly (D,L-lactic acid) macroporous guidance scaffolds seeded with Schwann cells genetically modified to secrete a bi-functional neurotrophin implanted in the completely transected adult rat thoracic spinal cord. Biomaterials.2006;27:430-442.
[17]Tuszynski MH,Peterson DA,Jadodhara Rag,et al.Fibroblasts genetically modified to produce nerve growth factor induce robust neuritic ingrowth after grafting to the spinal cord.Exp Neurol.1994;126:1.
[18]Tuszynski MH,Gabriel K,Gage FH,et al.Nerve growth factor delivery by gene transfer induce differential outgrowth of sensory,motor and noradrenergeic neurites after spinal cord injury.Exp Neurol.1996;127:157.
[19]Cao L, Liu L,Chen ZY, et al. Olfactory ensheathing cells genetically modified to secrete GDNF to promote spinal cord repair. Brain.2004; 127:535-549.
[20]Tuszynski MH,Meyers G,Nakahara Y,et al.Fibroblasts and schwann cells genetically modified to produce neurotrophic factors induce robust neuritic growth after transplantation to the spinal cord.Soc Neurosci Abstr.1994;20:10.
[21]Takami T, Oudega M, Bates ML, et al. Schwann Cell But Not Olfactory Ensheathing Glia Transplants Improve Hindlimb Locomotor Performance in the Moderately Contused Adult Rat Thoracic Spinal Cord. Neurosci.2002;22(15): 6670-6681.
[22]Oudega M, Moon LD, Almeida Leme RJ. Schwann cells for spinal cord repair. Braz J Med Biol Res.2005;38: 825-835.
[23]Oudega M, Gautier SE, Chapon P, et al. Axonal regeneration into Schwann cell grafts within resorbable poly(D-hydroxyacid) guidance channels in the adult rat spinal cord. Biomaterials. 2001; 22:1125-1136. |